| |
| |

|
| |
Links to previous articles
at the end of this article
|
The
first
article
in this thread summarized the seven factors that
cause failure, as well as the seven critical factors for success with
regard to Business Information System implementation.
These factors are vital in
understanding situations such as those that have recently
occurred at BMW
and Bridgestone
, and numerous other
companies around the world.
They are vital to understanding why the business systems industry is,
in large measure, going in the wrong direction. There is
significant evidence that the industry is getting better and better at
doing the wrong things.
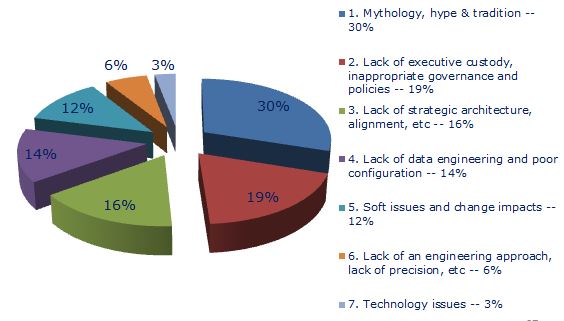
The figure below summarizes the seven factors causing failure.
|
| |
|
The Factors Causing Failure
|
 |
| |
This article presents the first two factors that cause failure in more
detail. These factors are Mythology and Lack of Effective
Executive Custody.
The percentages are roughly indicative of the relative frequency of these factors in causing sub-optimal and failed outcomes:
|
| |
|
1. Mythology, hype and tradition -- 30%
Mythology relates to a wide diversity of issues in terms of common
practices that give rise to major problems, but which cannot be
classified technically. The main components of mythology are:
|
| |
|
1.1. Any implementation firm will do
Different implementation consultants will achieve radically different
results. Every piece of software in existence can be configured
well and therefore utilized in high value ways, or it can be configured
badly and, in many cases fail to work at all. If the effectiveness
of implementation is scored in terms of business value on a scale of 0
to 100, the most effective implementation will deliver a business
outcome of 100. The majority of implementations are scoring in the area
of about 5, whilst 100 probably does NOT exist anywhere on the planet
today. The worst implementations can and do destroy
businesses. This is not understood by most clients and therefore
implementers are selected on the basis of inappropriate criteria that
result in highly sub-optimal outcomes.
|
| |
|
1.2. Hype and technology obsession
A sales hype driven industry that punts technology and makes claims
that are unfounded, unprovable and seldom realized because
implementations are tackled in the sub-optimal manner mentioned
above. Uses terminology like "vanilla" that is totally meaningless
but which creates mystique.
|
| |
|
1.3. Lies and deception
Outright lies, an industry where a significant number of sales
proposals contain outright lies, deliberately understate costs, exclude
items in fine print against future "upselling", etc.
|
| |
|
1.4. Transfer of blame to the client
Much of the industry has a culture of blaming the
client. Projects are structured and run such that client personnel
are manipulated into playing roles and taking on responsibility that in
any other industries (e.g. construction) are the responsibility
of specialist contractor staff. When things go wrong, it is
always the clients' fault and the client has to pay.
|
| |
|
1.5. Tradition and failure to learn from mistakes
The problems that are experienced have been broadly the same for the
last twenty years at least. About 70% of projects fail
outright and never reach production. At most 5% meet client
expectations and these numbers have not changed or, according to some,
are getting worse. The industry fails to learn from its mistakes
and continues to seek to get better at things that do not work, rather
than from a perspective of making money.
|
| |
|
1.6. "Change of Scope"
The concept of "change of scope" is an almost universal ill, even
on supposedly fixed price contracts. The implementer determines
the requirement in a sloppy fashion, documents it in a sloppy fashion,
has the client "sign off" on it (in a sloppy fashion) and then, when it does
not work, hits the client with claims of "change in scope",, with
additional costs as an end result.
|
| |
|
1.7. Incompetence pays best
One of the reasons why the incompetence inherent in what
is described above does not go away is that it pays better than doing
the job right. A well configured and commissioned system
will require limited support, which can be provided by in-house
personnel. A badly configured system requires ongoing "expert" support because
nobody in the client organization really knows how the system works.
It also requires continuous custom development in order to provide
answers to problems that should be catered for by the core systems.
By doing this implementation houses generate substantial
"annuity income". This highly profitable incompetence makes it extremely
difficult for large sectors of the industry to change their approach.
|
| |
|
1.8. Inappropriate personnel
Because of the above phenomena it
is
not that important who does the work (it will be sub-optimal anyway)
and so personnel with limited relevant knowledge and experience are employed.
Frequently these under qualified personnel are allocated to
the project full time for months. This gives rise to something
that I call "the audit model". System configuration and commissioning is fundamentally
an engineering endeavour, but it is seldom run
like that. Where engineers are involved in business systems projects,
they are often sucked into the wrong thinking of those who
subscribe to the bad practices described in this and other sections.
|
| |
|
1.9. Process obsession
One
of the greatest myths relates to "business process" -- really
business workflow. We are going to demolish the bridge and build a
massively bigger and better bridge and associated infrastructure, so we
undertake detailed measurements of the old winding road through the
gorge in order to determine how to build the new bridge over the
gorge. This is an interesting money printing phenomenon.
What is required is "strategic discovery", understand the essence of
why the organization exists and how it thrives. This should be
coupled to headline documentation of the current "way we do things round
here" in enough detail to inform the new design.
Then design the new solution to achieve the long term goals of
the business (five years plus) with strategic essence (thrive)
focus. Yes, we do need to know how the business functions, but the
most important consideration is how we want it to function in the future,
and this should be prescribed by the executives and senior managers of
the organization as part of the solution design. Detailed
flow charting, "swim lanes" and the like are a total waste of time
and money. Remember that "thrive" is about gut issues, intuition, not
workflow so "process" is simply not as important as the industry
believes.
|
| |
|
Mythology -- Summing Up
These factors individually and
collectively result in the client being intimidated and
frequently "bamboozled" into paying unnecessarily and
for unproductive and unnecessary services that produce
little or nothing of lasting consequence. In many
cases client expectations have been "dumbed down" over
the years. Robust
procurement methods
coupled to tough contracts and certification of compliance are an
essential prerequisite to preventing Mythology from taking hold.
Ongoing monitoring of the project for signs of Mythology and rooting out
of Mythology when it occurs is also critical.
|
| |
|
2. Inappropriate or ineffective executive custody, governance and corporate policy -- 19%
The next most important factor giving rise to failure relates to
corporate leadership, executive custody, overall project and system
governance, and corporate and project policies. The major elements
of this factor are:
|
| |
|
2.1. Inappropriate executive sponsorship
Most business system implementations of any significance should be
implemented with a strong strategic, "thrive" focus. This
necessitates executive oversight. On a division specific project,
with little or no interaction with the rest of the business, the
divisional executive should be the sponsor. The moment that the
system straddles multiple business units, divisions or functions, the
human and business integration of the system becomes paramount.
As the Chief Executive is the custodian of the integrated view and
management of the business, it follows that the Chief Executive must be
the sponsor of any major integrated business information system
project. This is non-negotiable and failure to recognize and
respect this system principle contributes to many sub-optimal and failed
outcomes.
|
| |
|
2.2. Lack of a Strategic Systems Advisor to the sponsor
The strategic application of systems in the best interests of the
client should be directed by the Chief Executive or sponsor guided by a
part time or full time Strategic Advisor depending on the scale of the
project. The Advisor should be in a staff advisory position or a
contract position with little or NO line responsibility. They
should have decades of experience with the effective strategic
application of business information systems, and NO allegiance to
particular software products or implementers before a system and
implementer are chosen.
This role is comparable to the lead architect in the design of a
prestige office building. They take direction from the client
executive and give direction without fear or favour in the best
interests of the client. This person moderates and, where
necessary, counters and directs the implementer in terms of the optimal
strategic business outcome. They serve as a translator to the
sponsor and the business. The tension that results is a necessary
part of this role, and they must be supported by a strong Contract
Manager to handle conflict, as strategic thinkers are seldom good at
handling conflict themselves.
|
| |
|
2.3. Inappropriate management of the project
Various forms of inappropriate management occur:
|
| |
|
a. CIO or IT Manager drives the project
A corollary of the above is abdication of the running of the project,
including choice of system and appointment of implementers to the Chief
Information Officer or, worse still, the IT Manager. That person
is responsible for the line management of technology, infrastructure,
services and the like. They are generally not strategically
orientated and most have never operated at the strategic executive
level. They embark on a technology project instead of a strategic
systems project with frequently highly sub-optimal results. Where
this person IS strategically orientated they are under such pressure
with day to day line functions that they cannot devote the required time
to guiding the project strategically. This person can, however,
serve as Contract Manager.
|
| |
|
b. Chief Financial Officer drives the project
On integrated systems, given that the financial suite is a key element,
it is seductive to place the Chief Financial Officer in charge.
In most cases this is a mistake. Firstly, they have operational
day to day priorities that are inflexible and cannot give the required
time. Secondly, accountants are NOT trained in the type of
disciplines necessary to drive this type of project. Thirdly, many
CFOs focus too much on finance and downplay, and in many cases obstruct
the solution in terms of operational functions. Depending on the
project and the person the CFO can sometimes be a suitable Business Team
Leader.
|
| |
|
c. Lack of a strong Contract Manager
The client counterpart of the implementer Project Manager is the
Contract Manager. The Contract Manager provides tough but fair
management in terms of contract compliance, allocation of resources,
etc. This is a role that the CIO or IT Manager is generally well
equipped to perform.
|
| |
|
d. Lack of a strong Business Team Leader
The Business Team Leader is an executive or senior manager, depending
on the scale of the project, who is responsible for mobilizing the best
possible business input for design, configuration, testing and
commissioning. This person is concerned with the practical
engagement with the business, and the putting into operation of the
system at a practical level. They do NOT need to have systems
experience, but they DO need to understand the desired business
outcome. They rely on the strategic advisor and the implementer
technical team to guide them in terms of the effective implementation of
the system.
|
| |
|
e. Lack of Implementer executive input
Given that we are speaking of medium to large integrated business
information systems, it is vital that NOT only the business but the
implementer provide strategic level direction to the project. Any
project of any size should be led from the Implementer side by an
executive of the firm. As with the executive sponsor, this does
NOT require a large amount of time - rather quality time, assisted by
the rest of the Implementer team.
|
| |
|
2.4. Inappropriate policies
I have seen many projects fail because of inappropriate policies.
A project that commences predicated on a statement like "it must be
FRED" where "FRED" is your favourite brand name business system, or the
one you used in your last position, or the one your friend from school
uses, frequently ends up in difficulty. Firstly because the
critical thinking and negotiation do not take place up front.
Secondly because sometimes FRED is simply NOT the right system for the
business. Thirdly because little thought is given to the choice of
implementer, and they come by default with the package. In most
cases, choose the implementer most strategically suited to the business,
and then go with the system they recommend. There are many other
policies that can get in the way of an effective solution.
|
| |
|
2.5. Unworkable governance -- Project Schizophrenia -- Steering Committees
The project governance that is put in place is frequently
inappropriate and frequently results in what I term Project Schizophrenia -- more than
one person in charge. The two or more "heads" are expected to
resolve differences in approach "collegially". This does NOT work
and is a recipe for conflict. Of this, the "Steering Committee" is
one of the most inappropriate approaches. To understand why I say
this: consider whether you would remain on an aircraft that was to be
flown by a committee, or relocate to one that was flown by a
Captain. There must be unitary overall leadership and overall
accountability, another reason why on medium to large projects the
sponsor must be the CEO supported by the team that is indicated above.
|
| |
|
2.6. Lack of executive level engagement
Most business system projects are undertaken with little or no
executive engagement (active intellectual participation) resulting in
decisions that waste time and get in the way of the essence of the
business. On large integrated business information system projects
there must be a significant level of interaction and consultation at
the executive level. Again the strategic advisor to guide,
facilitate and translate in order to ensure that only necessary
executive level interactions take place, is absolutely critical.
|
| |
|
2.7. Inappropriate client direction
In some cases, generally as an outflowing of the above, one encounters a
situation where the client is giving inappropriate direction to the
implementer. With an effective contract there are matters that are
entirely the contractor's (implementer's) responsibility and others
that are the client's -- these responsibilities must be clearly
delimited. Where they are NOT, all sorts of problems result.
|
| |
|
To follow
3. Lack of effective strategic alignment and strategic solution architecture -- 16%
4. Lack of Precision Configuration -- 14%
5. Failure to address soft issues, business engagement and change impacts -- 12%
6. Lack of an Engineering Approach -- 6%
7.
Technology Issues -- sub-optimal or defective software, hardware, network, etc -- 3%
The Critical Factors for
Success
1. Effective Executive Custody -- 25%
2.
Effective Strategic definition and alignment -- the Essence of the business -- 22%
3. Effective engineering solution design and implementation approach -- 17%
4. Effective Precision Configuration -- 16%
5. Effective Business Simulation Laboratory operation -- 12%
6. Effective business integration, training, change facilitation, process specification -- 6%
7. Reliable technology -- 2%
|
| |
|
Conclusion
Your
investment in a major business
information system, is one of the most far reaching projects your business
is likely to ever undertake. If you address the factors discussed above, together
with the other factors causing failure, as well as the Critical Factors
for Success, you will experience material beneficial impact.
I offer advisory services with regard to the application of these
principles, and would be delighted to discuss how I might be of
assistance to your business. I also offer a light touch diagnostic
service to diagnose the root cause of problems and how to fix them for
both operational systems and projects that are not meeting expectations.
Yours faithfully,
Dr James Robertson
PrEng
James A Robertson and Associates Limited
Assisting clients to thrive through effective and efficient application of Business Information Systems
Landline: +44 (0) 207-059-0007
|
| |
|
Previous articles:
The following articles are available in this series:
|
| |
|
Strategic Essence -- The Missing Link in Business Information Systems
A discussion of how strategic essence should inform all business
improvement projects and particularly business information system
projects. This thread is intended to discuss the analysis of
strategy, the planning of strategy and feeding strategy through into
business system specifications and the management of projects.
Articles to date include:
Summary
1:
Strategy Defined
2:
Differentiation
3:
The Essence IS Different
Determining
Strategic Essence
|
| |
|
The Real Issues in Business Information Systems
A discussion as to why business information system (and other business
improvement projects) fail to deliver on expectations or fail outright,
together with discussion of the critical factors that must be taken into
account in order to achieve successful outcomes. This thread is
intended to progressively discuss more hands-on specifics of achieving
high value outcomes and builds on the Strategic Essence series.
Articles to date include:
Introduction
|
| |
|
Strategically Enriching your Business Information Systems
Discussion of practical specific measures that can be taken in order to
greatly improve the information yield of business information systems
at both the operational and executive strategic level. A number of
simple steps that can be taken immediately and more complex measures
that can be taken over time. This thread is intended to discuss
increasing business system and data warehouse value yield using
techniques that lead to significantly improved business intelligence
capability, including support for the ability to "obtain answers to
questions we had not previously thought to ask". This builds on
the content in the Strategic Essence and Real Issues threads.
Articles to date include:
Introduction
|
| |
|
Robust Business Information Systems Procurement
In order to fully apply the methods and principles discussed in the
threads above with regard to new systems it is vital that a robust and
effective approach to procurement is applied. This requires a
tough procurement approach directed at achieving a tough business
outcomes orientated project that ensures a high value outcome.
This thread is intended to discuss the components of such a procurement
approach, including the individual documents and process that make up
the approach. Thereafter the components will be discussed in more
detail. Articles to date include:
Introduction Part 1
|
|
|
|